Function of Cytoplasm in Human cells
 All living organisms on earth consists of cells which are the basic units of life. Based on their function, cells are categorized into different types of cells, the somatic cells and the reproductive cells. Each cell has a nucleus and a jellylike watery substance that is 80% water that occupies the remaining part of the cell. This is called Cytoplasm. The cytoplasm holds different parts of the cell's organelles together. Cytoplasm was first discovered first in 1835 but the discovery is not credited to a single person as many biologists and researchers have contributed to the knowledge on Cytoplasm.
All living organisms on earth consists of cells which are the basic units of life. Based on their function, cells are categorized into different types of cells, the somatic cells and the reproductive cells. Each cell has a nucleus and a jellylike watery substance that is 80% water that occupies the remaining part of the cell. This is called Cytoplasm. The cytoplasm holds different parts of the cell's organelles together. Cytoplasm was first discovered first in 1835 but the discovery is not credited to a single person as many biologists and researchers have contributed to the knowledge on Cytoplasm.
What is the Structure of Cell?
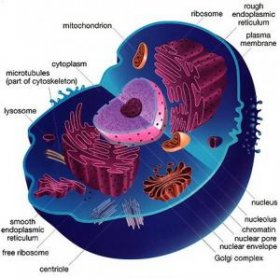
Each cell in our body can be divided into three parts. For example, blood cell, reproductive cell or brain cells all have all the three parts and a membrane through which nutrition is absorbed inside and the toxins are expelled outside. The liquid or gooey substance which lies between the outer membrane and the nucleus which is at the center is Cytoplasm. The main genetic components of the cell, DNA, chromosomes, and nucleic acid are located inside the nucleus. Cytoplasm mostly constitutes of water(80%) and various organelles. These organelles contain vitamins, ions, proteins, nucleic acids, sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and carbohydrates which are suspended in the gel like cytoplasm. The major functions of cells such as, expansion of You do not have access to view this node, growth and replication happen in the Cytoplasm.
What is the Function of Cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm being the main part of a cell, any abnormality in the contents of cytoplasm can be fatal and such living organisms do not live for long as it is the main platform for all biochemical reactions which are essential for sustenance of life. It provides suspension solution for the organelles and the cytoskeleton gives shape to the cell due to which in and out movement through the membrane is made possible. Organelles like mitochondria are incapable of breaking down glucose to form pyrovate which is essential for producing energy. The cytoplasm and the enzymes within it break down the macromolecules into small portions to facilitate energy production for the mitochondria’s of all the cells. Cytoplasm plays an important role in the process of glycolysis as well as in the synthesis of fatty acids, amino acid and sugar. Other essential functions which are carried out in the cytoplasm include protein synthesis, anaerobic glycosis, cytokinesis, cell You do not have access to view this node.
What is the Difference between Eukaryotic cell and Prokaryotic cell?
There are two different types of cells,
Prokaryotic cells are considered to be the primitive type of cells. Eukaryotic cells have evolved from the prokaryotic cells. And even though the eukaryotic cells have evolved, the prokaryotic cells have still retained their importance. Bacteria and Archaea that Prokaryotic cells do not have a bounded membrane and nucleus but do have the plasma membrane. These cells are mostly single celled and reproduce by binary fission.
Eukaryotic cells are much more complex and can be single celled or multi celled with nucleus in the center. Most of the living organisms comprise of eukaryotic cells. Some examples are plants, animals, fungi and protists. These cells can reproduce in several ways including mitosis and meiosis.
What is the Cytoplasm further divided into?
Cytoplasm can be divided into: Cytosol, organelles and cytoplasmic inclusions. Cytosol is a gelatinous material and most of the space in Cytoplasm when an organelle is not present. Cytosol comprises of salt, water, cytoskeleton filaments and organic molecules. The cells get their shape due to the protein filaments present in the cytoskeleton which also comprises of different fatty acids, enzymes, amino acids and sugar. Cytosol covers more than 70% of cell space and small percentage of proteasomes, ribosomes and soluble proteins are present in this part of Cytoplasm.
What are the different Organelles in the Cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm has cell components like endoplasmic reticulum, lysomes, mitochondria and Golgi apparatus. In the plant cells chloroplasts too are found in the organelles of cytoplasm which has a periphery surrounded by fatty membrane. Another organelle present in the cytoplasm-endoplasmic reticulum performs different functions such as production of steroids, synthesis and transport of proteins, producing and storing glycogen. Golgi apparatus performs the function of modifying, packaging, transporting, as well as processing of macromolecules such as lipids and proteins. The lysomes present in the suspension of cytoplasm comprise of digestive enzymes which digest food, damaged organelles as well as bacteria and virus.